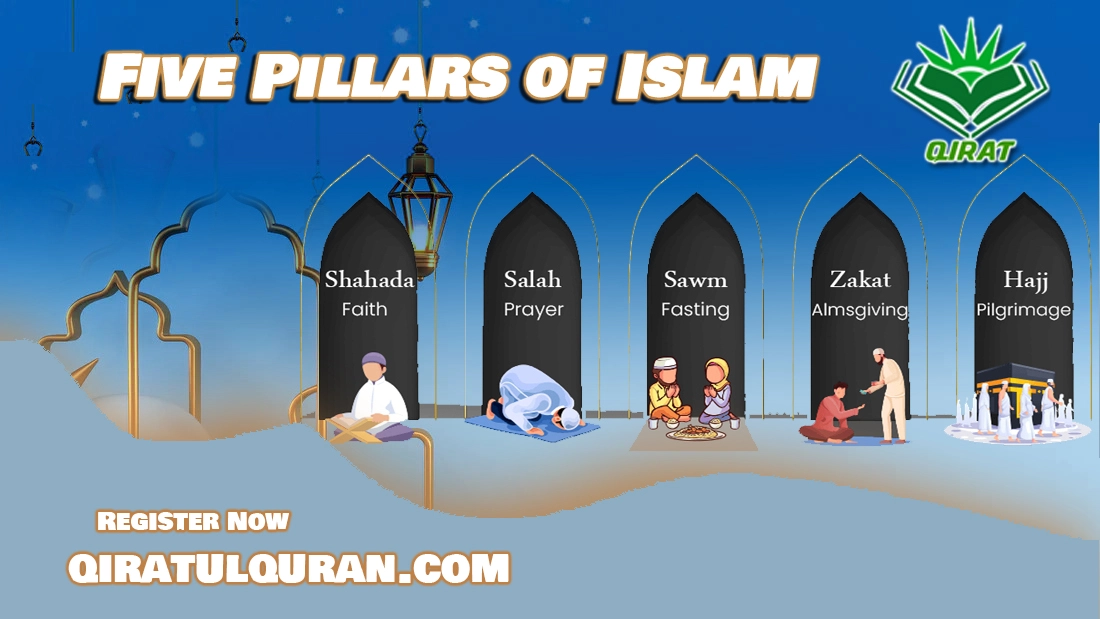
Islam is a religion that is based on the belief in one God and the teachings of the Prophet Muhammad. Its fundamental beliefs are encapsulated in the Five Pillars of Islam, which represent the core of the Islamic faith. These pillars are considered mandatory for every Muslim to follow in order to achieve salvation and build a strong connection with God. In this article, we will explore the Five Pillars of Islam and understand their significance in the Islamic faith.
Shahada – The Declaration of Faith
Shahada is the first and most fundamental of the Five Pillars of Islam. It is the declaration of faith that every Muslim must proclaim to become a Muslim. The Shahada is a simple yet powerful statement: “There is no god but Allah, and Muhammad is his messenger.” This declaration affirms the belief in the oneness of God and the prophethood of Muhammad.
How is Shahada Practiced?
Muslims declare the Shahada by reciting it out loud, preferably in the presence of witnesses. This declaration is usually done during the initiation ceremony of new Muslims, called the Shahada ceremony. Muslims are expected to recite the Shahada daily as a reminder of their faith and belief in God.
Salah – The Five Daily Prayers
Salah is the second pillar of Islam and requires Muslims to perform five daily prayers at specific times of the day. These prayers are mandatory and must be performed facing the Kaaba in Mecca. The five daily prayers are Fajr, Dhuhr, Asr, Maghrib, and Isha.
How is Salah Practiced?
Muslims perform the daily prayers by first performing Wudu, the Islamic ritual of cleansing oneself. They then perform the prayer by reciting verses from the Quran in a specific sequence of standing, bowing, prostrating, and sitting. The prayers can be performed individually or in the congregation, with the Friday prayer being the most important.
Zakat – The Obligatory Charity
Zakat is the third pillar of Islam and requires Muslims to give a portion of their wealth to the needy and the poor. Zakat is a mandatory charity and is considered a means of purifying one’s wealth and sharing it with those in need.
How is Zakat Practiced?
Muslims are required to pay Zakat annually, which is calculated as 2.5% of their net wealth. This wealth can include cash, gold, silver, and other assets. The collected Zakat is distributed among the needy and the poor in the form of food, clothing, shelter, and other basic necessities of life.
Sawm – The Fasting during Ramadan
Sawm is the fourth pillar of Islam and requires Muslims to fast during the holy month of Ramadan. Fasting is considered a means of purifying the soul and gaining closer proximity to God.
How is Sawm Practiced?
Muslims are required to abstain from food, drink, and other physical needs from dawn until dusk during the month of Ramadan. Fasting during Ramadan is mandatory for all healthy adult Muslims except for those who are exempted due to health reasons or other valid reasons.
Hajj – The Pilgrimage to Mecca
Hajj is the fifth and final pillar of Islam, and it refers to the pilgrimage to Mecca that all able-bodied Muslims are required to perform at least once in their lifetime. Hajj is a journey of spiritual and physical significance, as it represents the unity of Muslims from all over the world and is a means of seeking forgiveness and attaining spiritual purity. The rituals of Hajj commemorate the life of Prophet Abraham and his family and require Muslims to perform a series of acts, including wearing the Ihram, circling the Kaaba, standing at the plains of Arafat, throwing pebbles at Satan, and sacrificing an animal. The pilgrimage to Mecca is a deeply spiritual experience for Muslims, and it represents the culmination of their faith journey.
How is Hajj Practiced?
Hajj is performed during the Islamic month of Dhu al-Hijjah and requires Muslims to perform a series of rituals that commemorate the life of Prophet Abraham and his family. The rituals include wearing Ihram, a white garment that signifies purity and equality, circling the Kaaba, standing at the plains of Arafat, throwing pebbles at Satan, and sacrificing an animal.
Why is Hajj Significance?
Hajj is considered the pinnacle of the Islamic faith and is a means of seeking forgiveness and attaining spiritual purity. It also represents the unity of Muslims from all over the world, regardless of their race, ethnicity, or social status.
FAQs:
Q. What happens during the Shahada ceremony?
A. During the Shahada ceremony, new Muslims declare the Shahada in the presence of witnesses and officially become Muslims.
Q. Can Muslims perform Salah anywhere?
A. Muslims can perform Salah anywhere, as long as they face the Kaaba in Mecca.
Q. How is Zakat different from other forms of charity?
A. Zakat is a mandatory charity that is required to be given annually, while other forms of charity are voluntary.
Q. What is the significance of Ramadan in Islam?
A. Ramadan is considered a holy month in Islam, and fasting during this month is considered a means of gaining closeness to God and purifying the soul.
Q. What is the significance of the pilgrimage to Mecca?
A. The pilgrimage to Mecca represents the unity of Muslims and is a means of seeking forgiveness and attaining spiritual purity.
Conclusion:
The Five Pillars of Islam represent the fundamental beliefs that define the Islamic faith. They represent the core values of Islam, including faith, prayer, charity, fasting, and pilgrimage. Muslims are required to follow these pillars as a means of seeking closeness to God and attaining spiritual purity. Understanding the significance of these pillars is crucial in understanding the Islamic faith and its beliefs.



Pingback: Online Fiqh Course (Islamic Jurisprudence)